A) arthropods evolved before vertebrates did
B) extant terrestrial arthropods are better adapted to terrestrial life than are extant terrestrial vertebrates
C) vertebrates evolved from arthropods
D) arthropods have had more time to coevolve with land plants than have vertebrates
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do animals ranging from corals to monkeys have in common?
A) a mouth and an anus
B) number of embryonic tissue layers
C) some type of body symmetry
D) presence of Hox genes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which tissue type or organ is not correctly matched with its germ layer tissue?
A) nervous-mesoderm
B) muscular-mesoderm
C) stomach-endoderm
D) skin-ectoderm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is (are) unique to animals?
A) the structural carbohydrate, chitin
B) nervous system signal conduction and muscular movement
C) heterotrophy
D) flagellated gametes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Soon after the coelom begins to form, a researcher injects a dye into the coelom of a deuterostome embryo. Initially, the dye should be able to flow directly into the ________.
A) blastopore
B) blastocoel
C) archenteron
D) pseudocoelom
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals What conclusion can best be drawn from the data in the table?
A) Land animals have more Hox genes than do those that live in water.
B) All bilaterian phyla have had the same degree of expansion in their numbers of Hox genes.
C) The expansion in number of Hox genes throughout vertebrate evolution cannot be explained merely by three duplications of the ancestral vertebrate Hox cluster.
D) Extant insects all have seven Hox genes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The protostome developmental sequence arose just once in evolutionary history, resulting in two main subgroups-Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa. What does this finding suggest?
A) These two subgroups have a common ancestor that was a deuterostome.
B) The protostomes are a polyphyletic group.
C) Division of these two groups occurred after the protostome developmental sequence appeared.
D) The lophotrochozoans are monophyletic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Both animals and fungi are heterotrophic. What distinguishes animal heterotrophy from fungal heterotrophy is that most animals derive their nutrition by ________.
A) preying on animals
B) ingesting materials
C) consuming living, rather than dead, prey
D) using enzymes to digest their food
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher is trying to construct a molecular-based phylogeny of the entire animal kingdom. Assuming that none of the following genes are absolutely conserved, which of the following would be the best choice on which to base the phylogeny?
A) genes involved in chitin synthesis
B) collagen genes
C) genes involved in directing segmentation development
D) genes involved in eye-lens synthesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cadherin proteins help animal cells stick (adhere) to each other. Choose which statement about cadherin in cancer cells that are metastasising (spreading) throughout a patient's body is most likely correct.
A) Cadherin proteins in metastasising cancer cells are likely to have mutations that make them less "sticky".
B) Cadherin proteins in metastasising cancer cells are likely to have mutations that make them more "sticky".
C) Mutations in cadherin proteins are unlikely to affect the metastasising of cancer cells.
D) Mutations in cadherin proteins accumulate at a constant rate that can be measured by a molecular clock.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The last common ancestor of all animals was probably a ________.
A) unicellular chytrid
B) multicellular algae
C) multicellular fungus
D) flagellated protist
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student encounters an animal embryo at the eight-cell stage. The four smaller cells that comprise 1 hemisphere of the embryo seem to be rotated 45° and to lie in the grooves between larger, underlying cells. If we were to separate these eight cells and attempt to culture them individually, then what is most likely to happen?
A) All eight cells will die immediately.
B) Each cell may continue development, but only into a nonviable embryo that lacks many parts.
C) Each cell may develop into a full-sized, normal embryo.
D) Each cell may develop into a smaller-than-average, but otherwise normal, embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why might researchers choose to use molecular data (such as ribosomal RNA sequences) rather than morphological data to study the evolutionary history of animals?
A) Molecular data can be gathered in the lab, while morphological data must be gathered in the field.
B) Molecular data can be used to give an estimate of the time since two groups split.
C) Morphological changes usually do not result from molecular changes.
D) Some phyla vary too widely in morphological characteristics to be classified accurately.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the characteristics unique to animals is
A) gastrulation.
B) multicellularity.
C) sexual reproduction.
D) flagellated sperm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 As you are on the way to Tahiti for a vacation, your aeroplane crash lands on a previously undiscovered island. You soon find that the island is teeming with unfamiliar organisms, and you, as a student of biology, decide to survey them (with the aid of the Insta-Lab Portable Laboratory you brought along in your suitcase) . You select four organisms and observe them in detail, making the notations found in the figure.
-Which organism would you classify as an animal?
As you are on the way to Tahiti for a vacation, your aeroplane crash lands on a previously undiscovered island. You soon find that the island is teeming with unfamiliar organisms, and you, as a student of biology, decide to survey them (with the aid of the Insta-Lab Portable Laboratory you brought along in your suitcase) . You select four organisms and observe them in detail, making the notations found in the figure.
-Which organism would you classify as an animal?
A) organism A
B) organism B
C) organism C
D) organism D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
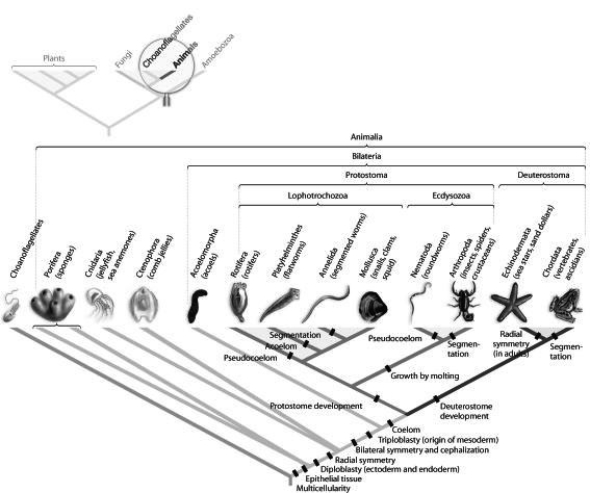 -Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals, according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in the figure?
-Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals, according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in the figure?
A) coelom
B) bilateral symmetry
C) segmentation
D) protostome development
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One hypothesis suggests that the Cambrian explosion was caused by the rise of predator-prey relationships. This hypothesis is best supported by an increased incidence of which of the following fossil traces?
A) worm burrows
B) larger animals
C) organic material
D) hard parts
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student encounters an animal embryo at the eight-cell stage. The four smaller cells that comprise 1 hemisphere of the embryo seem to be rotated 45° and to lie in the grooves between larger, underlying cells. This embryo may potentially develop into a(n) ________.
A) turtle
B) earthworm
C) star fish
D) sea urchin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a scientist describes the "body plan" of a phylum, he or she is implying that ________.
A) organisms direct their own evolution in order to maximise their success
B) animals evolve according to a pre-ordained plan
C) the body shapes we see now have been more successful than others in the past
D) mutations have arisen that allow only some shapes to be produced
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 - Which of the following pairs of animals show that animals with widely different adult features can be each other's closest relatives?
- Which of the following pairs of animals show that animals with widely different adult features can be each other's closest relatives?
A) Annelida and Nematoda
B) Chordata and Echinodermata
C) Cnidemia and Ctenophora
D) Annelida and Rotifera
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 67
Related Exams