A) break genomic DNA at random sites
B) map the position of cloned DNA fragments
C) randomly select DNA primers and hybridise these to random positions of chromosomes in preparation for sequencing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conclusions has led to the comparison between the number of human genes and those of other animal species?
A) The density of the human genome is far higher than in most other animals.
B) The number of proteins expressed by the human genome is far greater than the number of its genes.
C) Most human DNA consists of genes for protein, tRNA, rRNA, and miRNA.
D) The genomes of most other organisms are significantly smaller than the human genome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using modern techniques of sequencing by synthesis and the shotgun approach, sequences are assembled into chromosomes by ________.
A) placing them on previously generated genetic maps
B) cloning them into plasmid vectors
C) computer analysis looking for sequence overlaps
D) cloning them into plasmid vectors, placing them on previously generated genetic maps, followed by computer analysis looking for sequence overlaps
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bioinformatics includes all of the following except
A) using computer programs to align DNA sequences.
B) using DNA technology to combine DNA from two different sources in a test tube.
C) developing computer-based tools for genome analysis.
D) using mathematical tools to make sense of biological systems.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans, the embryonic and foetal forms of haemoglobin have a higher affinity for oxygen than that of adults. Why is this the case?
A) Nonidentical genes produce different versions of globins during development.
B) Pseudogenes interfere with gene expression in adults.
C) The attachment of methyl groups to cytosine following birth changes the type of haemoglobin produced.
D) Histone proteins change shape during embryonic development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two eukaryotic proteins have one domain in common but are otherwise very different. Which of the following processes is most likely to have contributed to this similarity?
A) gene duplication
B) alternative splicing
C) exon shuffling
D) random point mutations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of genes or gene families may be created by mutations that occur in one member of a gene pair that arose from gene duplication?
A) only a pseudogene
B) only a gene with a new function
C) only a gene family with two distinct but related members
D) a pseudogene, a gene with a new function, and a gene family with two distinct but related members
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is it more difficult to identify eukaryotic genes than prokaryotic genes using genomic techniques?
A) The proteins are larger in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes.
B) The coding portions of genes in eukaryotes are shorter than in prokaryotes.
C) There are no start codons in eukaryotic genes.
D) There are introns in eukaryotic genes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes one characteristic of a multigene family?
A) A multigene family includes multiple genes whose products must be coordinately expressed.
B) A multigene family includes genes whose sequences are very similar and that probably arose by duplication.
C) A multigene family includes a gene whose exons can be spliced in a number of different ways.
D) A multigene family includes a highly conserved gene found in a number of different species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homeotic genes
A) encode transcription factors that control the expression of genes responsible for specific anatomical structures.
B) are found only in Drosophila and other arthropods.
C) are the only genes that contain the homeobox domain.
D) encode proteins that form anatomical structures in the fly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bioinformatics can be used to scan for short sequences that specify known mRNAs, called ________.
A) expressed sequence tags
B) multigene families
C) proteomes
D) short tandem repeats
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biologists now routinely test for homology between genes in different species. If genes are determined to be homologous, how are they related to each other?
A) by descent from a common ancestor
B) because of convergent evolution
C) by chance mutations
D) in function but not structure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the sequence of a cDNA has matches with DNA sequences in the genome, then this genomic DNA could be described by which of the following statements?
A) The sequence codes for a protein.
B) The sequence codes for an rRNA.
C) The sequence is part of an intron.
D) The sequence is a regulatory sequence.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What can proteomics reveal that genomics cannot?
A) the number of genes characteristic of a species
B) the patterns of alternative splicing
C) the set of proteins present within a cell or tissue type
D) the movement of transposable elements within the genome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After finding a new medicinal plant, a pharmaceutical company decides to determine if the plant has genes similar to those of other known medicinal plants. What would annotation of the genome of this plant allow the company to determine?
A) what proteins are produced by the plant
B) what mRNA transcripts are produced by the plant
C) identify genes and determine their functions
D) identify the location of mRNA within the plant cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which of the following processes does exon shuffling occur?
A) splicing of DNA
B) DNA replication
C) meiotic recombination
D) translation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
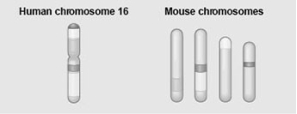 The figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
Which of the following statements describes the result of the movement of these blocks?
The figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
Which of the following statements describes the result of the movement of these blocks?
A) During evolutionary time, these sequences have separated and have returned to their original positions.
B) DNA sequences within these blocks have become increasingly divergent.
C) Sequences represented have duplicated at least three times.
D) Chromosomal translocations have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fragments of DNA have been extracted from the remnants of extinct woolly mammoths, amplified, and sequenced. How can these fragments of DNA now be used?
A) to introduce certain mammoth traits into relatives, such as elephants
B) to clone live woolly mammoths
C) to understand the reasons why mammoths went extinct
D) to better understand the evolutionary relationships among members of related taxa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bioinformatics includes ________. I. using computer programs to align DNA sequences II. creating recombinant DNA from separate species III. developing computer-based tools for genome analysis IV. using mathematical tools to make sense of biological systems
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) II and IV
D) I, III, and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is "metagenomics"?
A) genomics as applied to a species that most typifies the average phenotype of its genus
B) the sequencing of one or two representative genes from several species
C) the sequencing of only the most highly conserved genes in a lineage
D) sequencing DNA from a group of species from the same ecosystem
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 44
Related Exams