A) Some tRNAs have anticodons that recognise four or more different codons.
B) The rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA are flexible.
C) Many codons are never used, so the tRNAs that recognise them are dispensable.
D) The DNA codes for all 61 tRNAs, but some are then destroyed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of RNA processing?
A) Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus.
B) Nucleotides may be added at both ends of the RNA.
C) Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing.
D) RNA splicing can be catalysed by spliceosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Post-translational modifications of proteins may include which of the following processes?
A) removal of introns
B) addition of a 5′ cap
C) addition of a poly-A tail
D) addition of carbohydrates to form a glycoprotein
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the significance of the TATA box in the promoters of eukaryotes?
A) It is the recognition site for the binding of a specific transcription factor.
B) It sets the reading frame of the mRNA during translation.
C) It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding during translation.
D) It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding during transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following one-base point mutations with respect to their likelihood of affecting the structure of the corresponding polypeptide (from most likely to least likely) . 1) insertion mutation deep within an intron 2) substitution mutation at the third position of a codon in an exon 3) substitution mutation at the second position of a codon in an exon 4) deletion mutation within the first exon of the gene
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 2, 1, 4, 3
D) 3, 1, 4, 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume which of the following statements to be true?
A) A gene from an organism can theoretically be expressed by any other organism.
B) DNA was the first genetic material.
C) The same codons in different organisms translate into different amino acids.
D) Different organisms have different types of amino acids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is the most current description of a gene?
A) A unit of heredity that causes formation of a phenotypic characteristic.
B) A DNA subunit that codes for a single complete protein.
C) A DNA sequence that is expressed to form a functional product: either RNA or polypeptide.
D) A discrete unit of hereditary information that consists of a sequence of amino acids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
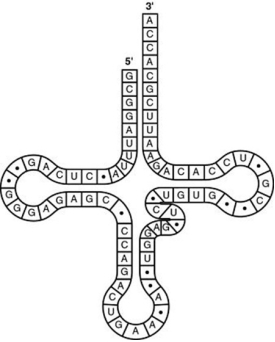 The figure represents tRNA that recognises and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) .
-Which codon on the mRNA strand codes for this amino acid?
The figure represents tRNA that recognises and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) .
-Which codon on the mRNA strand codes for this amino acid?
A) 5′-UGG-3′
B) 3′-GUG-5′
C) 5′-GUA-3′
D) 5′-UUC-3′
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following properties is associated with a protein that will be secreted from a eukaryotic cell?
A) It must be translated by a ribosome that remains free within the cytosol.
B) Its signal sequence must target it to the ER, after which it goes to the Golgi.
C) Its signal sequence must be cleaved off before the polypeptide can enter the ER.
D) Its signal sequence must target it to the plasma membrane, where it causes exocytosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is the first event to take place in translation in eukaryotes?
A) base pairing of activated methionine-tRNA to AUG of the messenger RNA
B) binding of the larger ribosomal subunit to smaller ribosomal subunits
C) the ribosome reaches a stop codon
D) the small subunit of the ribosome recognises and attaches to the 5′ cap of mRNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single base substitution mutation is likely to have a less deleterious effect when the base change exhibits which of the following results?
A) a stop codon
B) a codon that specifies the same amino acid as the original codon
C) an amino acid substitution that alters the tertiary structure of the protein
D) an amino acid substitution at the active site of an enzyme
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the central dogma, what is the intermediate molecule involved in the flow of information in a cell that should go in the blank? DNA → ________ → Proteins
A) mtDNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) tRNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the primary transcript in the nucleus of a prokaryotic cell compare to the functional mRNA?
A) the primary transcript is larger than the mRNA
B) the primary transcript is smaller than the mRNA
C) the primary transcript and the mRNA both contain introns
D) the primary transcript is the same size as the mRNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the function of a signal peptide?
A) It directs an mRNA molecule into the cisternal space of the ER.
B) It terminates translation of messenger RNA.
C) It helps target a protein to the ER.
D) It signals the initiation of transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How might a single base substitution in the sequence of a gene affect the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by the gene?
A) Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame would be unaffected.
B) The amino acid sequence would be substantially altered, because the reading frame would change with a single base substitution.
C) All amino acids following the substitution would be affected, because the reading frame would be shifted.
D) It is not possible for a single base substitution to affect protein structure, because each codon is three bases long.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes a ribozyme?
A) It is a catalyst that uses RNA as a substrate.
B) It is an RNA with catalytic activity.
C) It is an enzyme that catalyses the association between the large and small ribosomal subunits.
D) It is an enzyme that synthesises RNA as part of the transcription process.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs when termination of translation takes place?
A) The end of the mRNA molecule is reached.
B) A stop codon is reached.
C) The 5′ cap is reached.
D) The poly-A tail is reached.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecular structures contain codons?
A) a protein
B) mRNA
C) tRNA
D) rRNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experimental situation, a student researcher inserts an mRNA molecule into a eukaryotic cell after she has removed its 5′ cap and poly-A tail. Which of the following processes would you expect her to find to have occurred?
A) The mRNA is quickly converted into a ribosomal subunit.
B) The cell adds a new poly-A tail to the mRNA.
C) The mRNA attaches to a ribosome and is translated, but more slowly.
D) The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5′ end.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AAA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds the mRNA codon is ________.
A) TTT
B) UUA
C) UUU
D) AAA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams