A) complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon.
B) complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA.
C) the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid.
D) catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
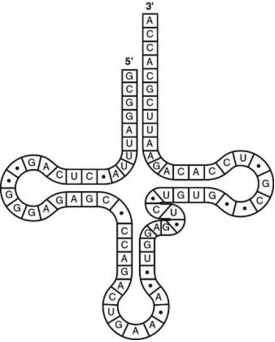 The tRNA shown in the figure has its 3′ end projecting beyond its 5′ end.
- Which of the following processes will occur at this 3′ end?
The tRNA shown in the figure has its 3′ end projecting beyond its 5′ end.
- Which of the following processes will occur at this 3′ end?
A) The amino acid binds covalently.
B) The excess nucleotides (ACCA) will be cleaved off at the ribosome.
C) The small and large subunits of the ribosome will attach to it.
D) The 5′ cap of the mRNA will become covalently bound.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics is directly related to the coding of a single amino acid during the process of translation?
A) The base sequence of the tRNA.
B) The amino acetyl tRNA synthase.
C) The three-base sequence of mRNA.
D) The complementarity of DNA and RNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs in prokaryotes but not in eukaryotes?
A) post-transcriptional splicing
B) transcription and translation occur simultaneously
C) translation in the absence of a ribosome
D) gene splicing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
B) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
C) the 5 caps are removed from the mRNA.
D) the DNA introns are removed from the template.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of a codon?
A) It may code for the same amino acid as another codon.
B) It never codes for more than one amino acid.
C) It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule.
D) It is the basic unit of the genetic code.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Once researchers identified DNA as the molecule responsible for transmitting heritable traits, they asked how information was transferred from the DNA in the nucleus to the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. Which of the following statements correctly describes the mechanism of information transfer in eukaryotes that accomplishes this task?
A) DNA from a single gene is replicated and transferred to the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis.
B) Messenger RNA is transcribed from a single gene and transfers information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis takes place.
C) Histone proteins in the chromosomes transfer information from the nucleus to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
D) Transfer RNA takes information from DNA directly to a ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
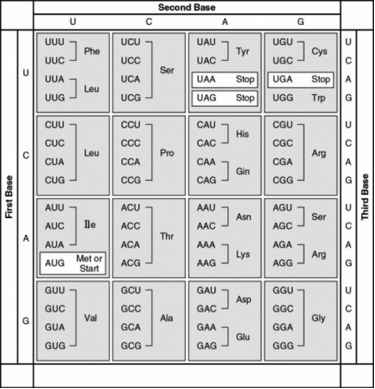 - What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5′-AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG-3′
- What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5′-AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG-3′
A) Met-Arg-Glu-Arg-Glu-Arg
B) Met-Glu-Arg-Arg-Glu-Leu
C) Met-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser
D) Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on specificity in the ________.
A) binding of ribosomes to mRNA
B) binding of the anticodon to small subunit of the ribosome
C) attachment of amino acids to rRNAs
D) binding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
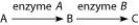 The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
- If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene encoding enzyme B would be able to grow on medium supplemented with which of the following nutrient(s) ?
The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
- If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene encoding enzyme B would be able to grow on medium supplemented with which of the following nutrient(s) ?
A) nutrient A only
B) nutrient B only
C) nutrient C only
D) nutrients A and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the elongation phase of translation, which site in the ribosome represents the location where a codon is being read?
A) E site
B) P site
C) A site
D) the large ribosomal subunit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5′-CCG-ACG-3′ (mRNA) . The following charged transfer RNA molecules (with their anticodons shown in the 3′ to 5′ direction) are available. Two of them can correctly match the mRNA so that a dipeptide can form. - Which of the following anticodons in the first tRNA to bind will complement this mRNA?
A) 3?-GGC-5?
B) 5?-GGC-3?
C) 5?-UGC-3?
D) 3?-UGC-5?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements about RNA processing is correct?
A) Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus.
B) Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing.
C) RNA splicing can be catalysed by tRNA.
D) A primary transcript is often much shorter than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
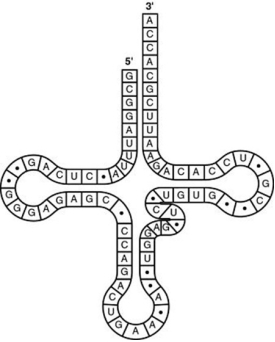 The figure represents tRNA that recognises and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) .
- What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule shown in the figure?
The figure represents tRNA that recognises and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) .
- What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule shown in the figure?
A) ionic bonding between phosphates
B) hydrogen bonding between base pairs
C) van der Waals interactions between hydrogen atoms
D) peptide bonding between amino acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes correctly describes alternative RNA splicing?
A) It is a mechanism for increasing the rate of translation.
B) It can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA.
C) It can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
D) It increases the rate of transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the termination of transcription in prokaryotes?
A) RNA polymerase transcribes through the polyadenylation signal, causing proteins to associate with the transcript and cut it free from the polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase transcribes through the terminator sequence, causing the polymerase to separate from the DNA and release the transcript.
C) Once transcription has initiated, RNA polymerase transcribes until it reaches the end of the chromosome.
D) RNA polymerase transcribes through a stop codon, causing the polymerase to stop advancing through the gene and release the mRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5′-AGT-3′. What would be the corresponding codon for the mRNA that is transcribed?
A) 3′-UCA-5′
B) 3′-UGA-5′
C) 5′-TCA-3′
D) 3′-ACU-5′
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
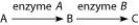 The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
-According to Beadle and Tatum's (1930s) hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
-According to Beadle and Tatum's (1930s) hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) It cannot be determined from the pathway.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotes, there are several different types of RNA polymerase. Which type is involved in transcription of mRNA for a globin protein?
A) RNA polymerase I
B) RNA polymerase II
C) RNA polymerase III
D) primase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would be the consequence of a mutation in a bacterial cell that produces a defective aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that attaches a lysine instead of the normal phenylalanine to tRNAs with the anticodon AAA?
A) None of the proteins in the cell will contain phenylalanine.
B) Proteins in the cell will include lysine instead of phenylalanine at amino acid positions specified by the codon UUU.
C) The cell will compensate for the defect by attaching phenylalanine to tRNAs with lysine-specifying anticodons.
D) The ribosome will skip a codon every time a UUU is encountered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 67
Related Exams