A) Telomerase will speed up the rate of cell proliferation.
B) Telomerase eliminates telomere shortening and retards ageing.
C) Telomerase shortens telomeres, which delays cellular ageing.
D) Telomerase would have no effect on cellular ageing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Semiconservative replication involves a template. What is the template?
A) single-stranded binding proteins
B) DNA polymerase
C) one strand of the DNA molecule
D) an RNA molecule
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a healthy eukaryotic cell, the rate of DNA repair is typically equal to the rate of DNA mutation. When the rate of repair lags behind the rate of mutation, what is a possible fate of the cell?
A) The cell can be transformed into a cancerous cell.
B) RNA may be used instead of DNA as inheritance material.
C) DNA replication will proceed more quickly.
D) DNA replication will continue by a new mechanism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describes one characteristic of histones?
A) Each nucleosome consists of two molecules of histone H1.
B) Histone H1 is not present in the nucleosome bead; instead, it draws the nucleosomes together.
C) The carboxyl end of each histone extends outward from the nucleosome and is called a 'histone tail'.
D) Histones are found in mammals, but not in other animals or in plants or fungi.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structural characteristics is most critical for the association between histones and DNA?
A) Histones are small proteins.
B) Histones are highly conserved (that is, histones are very similar in every eukaryote) .
C) There are at least five different histone proteins in every eukaryote.
D) Histones are positively charged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
E. coli cells grown on 15N medium are transferred to 14N medium and allowed to grow for two more generations (two rounds of DNA replication) . DNA extracted from these cells is centrifuged. What density distribution of DNA would you expect in this experiment?
A) one high-density and one low-density band
B) one intermediate-density band
C) one high-density and one intermediate-density band
D) one low-density and one intermediate-density band
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lists represents the order of increasingly higher levels of organisation of chromatin?
A) nucleosome, 30-nm chromatin fibre, looped domain
B) looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fibre, nucleosome
C) nucleosome, looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fibre
D) 30-nm chromatin fibre, nucleosome, looped domain
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In E. coli, to repair a thymine dimer by nucleotide excision repair, in which order do the necessary enzymes act?
A) nuclease, DNA polymerase, RNA primase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
C) DNA ligase, nuclease, helicase
D) nuclease, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of cells are affected most by telomere shortening?
A) only prokaryotic cells
B) only eukaryotic cells
C) cells in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
D) only animal cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics would you expect of a eukaryotic organism that lacks the enzyme telomerase?
A) A high probability of somatic cells becoming cancerous.
B) An inability to produce Okazaki fragments.
C) An inability to repair thymine dimers.
D) A reduction in chromosome length in gametes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the enzyme telomerase meet the challenge of replicating the ends of linear chromosomes?
A) It adds a single 5' cap structure that resists degradation by nucleases.
B) It causes specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands.
C) It catalyses the lengthening of telomeres, compensating for the shortening that could occur during replication without telomerase activity.
D) It adds numerous GC pairs, which resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are 'telomeres'?
A) The structures that hold two sister chromatids together.
B) Enzymes that elongate the DNA strand during replication.
C) The sites of origin of DNA replication.
D) The ends of linear chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following investigators was (were) responsible for the discovery that in DNA from any species, the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine?
A) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
B) Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod
C) Erwin Chargaff
D) Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In analysing the number of different bases in a DNA sample, which result would be consistent with the base-pairing rules?
A) A = G
B) A + G = C + T
C) A + T = G + C
D) A = C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
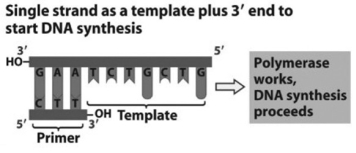 Referring to the figure, what bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds?
Referring to the figure, what bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds?
A) 5′ C, A, G, C, A, G, A 3′
B) 3′ T, C, T, G, C, T, G 5′
C) 5′ A, G, A, C, G, A, C 3′
D) 3′ G, T, C, G, T, C, T 5′
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the basis for the difference in how the leading and lagging strands of DNA molecules are synthesised?
A) The origins of replication occur only at the 5′ end.
B) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins work at the 5′ end.
C) DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3′ end of a pre-existing strand, and the strands are antiparallel.
D) DNA ligase works only in the 3′ → 5′ direction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describes the structure of a eukaryotic chromosome?
A) It is composed of a single strand of DNA.
B) It is constructed as a series of nucleosomes wrapped around two DNA molecules.
C) It has different numbers of genes in different cell types of an organism.
D) It is a single linear molecule of double-stranded DNA plus proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around
A) histones.
B) ribosomes.
C) polymerase molecules.
D) a thymine dimer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describes the differences between DNA replication in prokaryotes and DNA replication in eukaryotes?
A) Prokaryotic chromosomes have histones, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes do not.
B) Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many.
C) The rate of elongation during DNA replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes.
D) Prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but eukaryotes do not.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication?
A) It synthesises RNA nucleotides to make a primer.
B) It joins Okazaki fragments together.
C) It unwinds the parental double helix.
D) It stabilises the unwound parental DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 65
Related Exams