A) It is recessive.
B) It is codominant.
C) It is dominant.
D) It is incompletely dominant.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
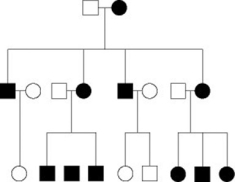 The pedigree in the figure shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely ________.
The pedigree in the figure shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely ________.
A) mitochondrial
B) sex-linked dominant
C) sex-linked recessive
D) autosomal dominant
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a syndrome?
A) A characteristic facial appearance.
B) A trait that leads to cancer at some stage in life.
C) A group of traits typically found in conjunction with a particular chromosomal aberration or gene mutation.
D) A specific characteristic that appears in conjunction with one specific aneuploidy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant-like organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type) : - The greatest distance among the three genes is between a and c. What does this mean?
A) Gene c is between a and b.
B) Genes are in the order: a-b-c.
C) Gene a is not recombining with c.
D) Gene a is between b and c.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does a recombination frequency of 50% indicate?
A) The two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes.
B) All of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the two parents.
C) The genes are located on sex chromosomes.
D) Abnormal meiosis has occurred.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are males more often affected by sex-linked traits than females?
A) Male hormones such as testosterone often alter the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
B) Female hormones such as oestrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
C) X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
D) Males are hemizygous for the X chromosome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
A) The gene involved is located on the Y chromosome.
B) The gene involved is located on the X chromosome.
C) The gene involved is located on an autosome, but only in males.
D) Other male-specific factors influence eye colour in flies.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally, only female cats have the tortoiseshell phenotype for fur colour. Which of the following statements explains this phenomenon?
A) A male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair colour.
B) The Y chromosome has a gene blocking orange colouration.
C) Only males can have Barr bodies.
D) Multiple crossovers on the Y chromosome prevent orange pigment production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
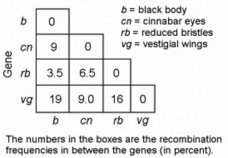 In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in the figure. Based on this information, what is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in the figure. Based on this information, what is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
A) rb-cn-vg-b
B) cn-rb-b-vg
C) b-rb-cn-vg
D) vg-cn-b-rb
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements would explain a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies in which more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring are produced?
A) The two genes are closely linked on the same chromosome.
B) The two genes are linked but on different chromosomes.
C) Recombination did not occur in the cell during meiosis.
D) Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The SRY gene is best described as ________.
A) a gene present on the X chromosome that triggers female development
B) an autosomal gene that is required for the expression of genes on the Y chromosome
C) a gene present on the Y chromosome that triggers male development
D) an autosomal gene that is required for the expression of genes on the X chromosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurrences describes how recombination between linked genes comes about?
A) Nonrecombinant chromosomes break and then rejoin with one another.
B) Independent assortment sometimes fails.
C) Linked genes travel together at anaphase.
D) Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons?
A) The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of the chromosome.
B) The relationship between recombination frequency and map units is different in every individual.
C) Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell cycle.
D) The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly different in every individual.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the reason that closely-linked genes are typically inherited together?
A) They are located close together on the same chromosome.
B) The number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes.
C) Alleles are paired together during meiosis.
D) Genes align that way during metaphase I of meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant-like organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type) : - What is the greatest benefit of having used a testcross for this experiment?
A) The homozygous recessive parents are obvious to the naked eye.
B) The homozygous parents are the only ones whose crossovers make a difference.
C) The phenotypes of the progeny reveal the allelic content of the gamete from the heterozygous parent.
D) All of the progeny will be heterozygous.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following phrases correctly defines what one map unit is?
A) The physical distance between two linked genes.
B) A 1% frequency of recombination between two genes.
C) 1 nanometer of distance between two genes.
D) The recombination frequency between two genes assorting independently.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumours. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following events might then occur to make the cancer worse?
A) an increase in nondisjunction
B) expression of inappropriate gene products
C) a decrease in mitotic frequency
D) failure of the cancer cells to multiply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their 20s. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition?
A) Women can never have this condition.
B) One-fourth of the daughters of an affected man would have this condition.
C) One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
D) Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A woman is found to have 47 chromosomes, including three X chromosomes. Which of the following statements describes her expected phenotype?
A) A female with masculine characteristics such as facial hair.
B) An apparent male who is sterile.
C) Healthy female of slightly above-average height.
D) A sterile female.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes what happens to a chromosome after a nonreciprocal translocation occurs?
A) A deletion of part of the chromosome occurs.
B) A duplication of part of the chromosome occurs.
C) Nondisjunction of pairs of homologous occurs.
D) A chromosome transfers a fragment but receives none in return.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 58
Related Exams