A) economy is in a deep recession.
B) MPC equals 1.
C) economy is already operating at full employment.
D) price level has fallen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
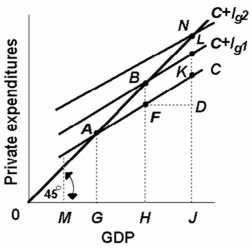 -Refer to the above diagram which applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment increases from Ig1 to Ig2, the equilibrium GDP will:
-Refer to the above diagram which applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment increases from Ig1 to Ig2, the equilibrium GDP will:
A) decrease by KD.
B) increase by HJ.
C) increase by KD.
D) increase by GH.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Planned investment equals saving:
A) at all levels of GDP.
B) at all below-equilibrium levels of GDP.
C) at all above-equilibrium levels of GDP.
D) only at the equilibrium GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
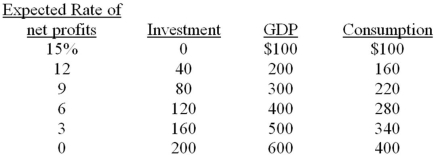 -Refer to the above information. In this economy a 3 percentage point decrease in the interest rate will:
-Refer to the above information. In this economy a 3 percentage point decrease in the interest rate will:
A) increase equilibrium GDP by $200.
B) increase equilibrium GDP by $100.
C) increase equilibrium GDP by $50.
D) decrease equilibrium GDP by $50.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a lump-sum income tax of $25 billion is levied and the MPS is 0.20, the:
A) saving schedule will shift upward by $5 billion.
B) consumption schedule will shift downward by $25 billion.
C) consumption schedule will shift downward by $20 billion.
D) consumption schedule will shift upward by $25 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
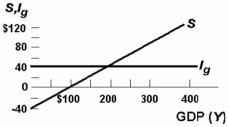 -Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the $200 level of GDP:
-Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the $200 level of GDP:
A) consumption will equal GDP.
B) planned investment will equal saving and unintended investment will be zero.
C) aggregate expenditures will exceed GDP, causing GDP to rise.
D) GDP will exceed aggregate expenditures, causing GDP to fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC in an economy is .75, a $1 billion increase in taxes will reduce the GDP by:
A) $1 billion.
B) $.75 billion.
C) $3 billion.
D) $4 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
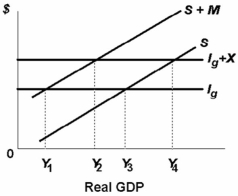 -In the above private open economy exports are __________ and imports are __________ domestic GDP:
-In the above private open economy exports are __________ and imports are __________ domestic GDP:
A) inversely related to, directly related to
B) independent of, inversely related to
C) independent of, dependent of
D) directly related to, independent of
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information is for a closed economy:
 -Refer to the above information. The introduction of $80 billion of government spending has:
-Refer to the above information. The introduction of $80 billion of government spending has:
A) lowered the multiplier from 2.5 to 2.0.
B) increased the multiplier from 2.5 to 3.0.
C) increased the multiplier from 2.0 to 2.5.
D) had no effect on the size of the multiplier.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The investment schedule tends to be relatively stable over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If aggregate expenditures exceed the domestic output in a private closed economy:
A) leakages will exceed injections.
B) planned investment will exceed saving.
C) unplanned investment in inventories will occur.
D) saving will exceed planned investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the dollar appreciates relative to foreign currencies, we would expect:
A) the multiplier to decrease.
B) a country's exports and imports to both fall.
C) a country's net exports to rise.
D) a country's net exports to fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Refer to the above diagram. The level of government spending:
-Refer to the above diagram. The level of government spending:
A) is equal to tax collections at each level of GDP.
B) is the same at all levels of GDP.
C) varies inversely with the level of GDP.
D) varies directly with the level of GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mixed closed economy:
A) government purchases and saving are injections, while investment and taxes are leakages.
B) taxes and government purchases are leakages, while investment and saving are injections.
C) taxes and savings are leakages, while investment and government purchases are injections.
D) taxes and investment are injections, while saving and government purchases are leakages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unplanned changes in inventories:
A) cause the economy to move away from the equilibrium GDP.
B) must be subtracted from planned investment to determine actual investment.
C) bring actual investment and saving into equality only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
D) bring actual investment and saving into equality at all levels of GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
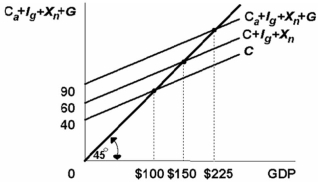
 -Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the $100 level of GDP:
-Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the $100 level of GDP:
A) aggregate expenditures will exceed GDP, causing GDP to fall.
B) planned investment will exceed saving, but actual investment will be equal to saving.
C) households will consume more than their income.
D) saving will be $40.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
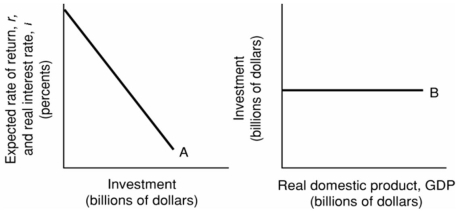 -Refer to the above diagrams. Other things equal, Curve B will shift upward when:
-Refer to the above diagrams. Other things equal, Curve B will shift upward when:
A) the level of GDP increases.
B) the interest rate increases.
C) curve A shifts to the left.
D) curve A shifts to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate expenditures model, a reduction in taxes may:
A) increase saving.
B) increase real GDP.
C) reduce unemployment.
D) do all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information below. The multiplier for this economy: 
A) is 2.
B) is 2.5.
C) is 3.
D) is 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Other: Pick-up
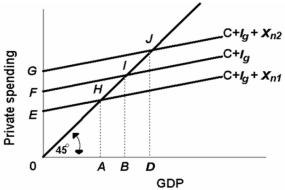
-Refer to the above diagram. If net exports are Xn2, the GDP in the open economy will exceed GDP in the closed economy by:
Other: Pick-up
-Refer to the above diagram. If net exports are Xn2, the GDP in the open economy will exceed GDP in the closed economy by:
A) AB.
B) AD.
C) FG.
D) BD.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 235
Related Exams