A) Less than 0.5 centimeters
B) 0.5 to 1 centimeter
C) 1 to 2 centimeters
D) 2 to 4 centimeters
E) 4 to 10 centimeters
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How are silt deposits called loess related to glaciers?
A) They accumulate in lakes trapped behind glaciers.
B) They form in lakes as the lakes dried up at the end of the ice ages.
C) They were deposited by large glacially caused floods in the Pacific Northwest.
D) They are wind-blown accumulations and commonly are derived from glaciers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the amount of ice on the planet increased to the amount that was present during the last glacial maximum,how much would it cause global sea level to fall? If you do not remember the approximate size of this rise,the volume of additional ice is 52,000,000 km3 and the surface area of the world's ocean is 361,000,000 km2.
A) Less than 10 centimeters
B) 10 centimeters to 1 meter
C) 1 meter to 10 meters
D) 10 meters to 50 meters
E) More than 50 meters
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What carved this U-shaped valley? 
A) A rapidly downcutting river
B) A slowly downcutting river
C) Wind
D) Glacier
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens when a glacier encounters the sea or a lake?
A) The ice is denser than water and so scrapes along the bottom.
B) White icebergs float but blue icebergs sink to the bottom.
C) Large blocks of ice collapse off the front of the glacier and become icebergs.
D) Rocks released from melted icebergs float on the water surface.
E) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the origin of curved ridges (R on this figure) in the Great Lakes area? 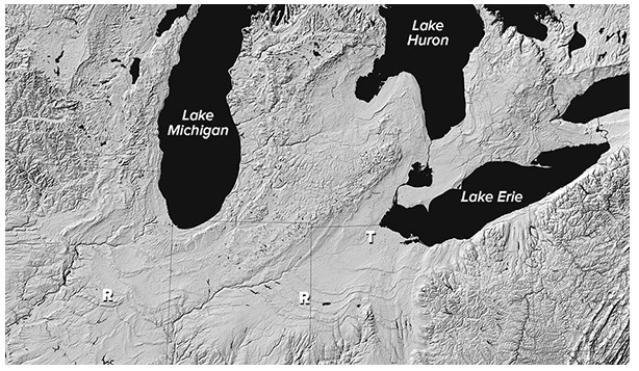
A) Folds produced during a continental collision
B) Paths of ancient rivers
C) Piles of sediment deposited by retreating glaciers
D) Remnants of a meteoroid impact
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is permafrost?
A) Curly crystals of frost that form early in the morning
B) Ice and snow that exist throughout the entire year
C) Ice and snow that are permanently in motion
D) The upper part of the ground that remains frozen throughout the year
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of glacier is shown in the center of this image? 
A) Ribbon glacier
B) Valley glacier
C) Low-elevation glacier
D) High-elevation glacier
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the origin of smooth troughs (T on this figure) cutting across the landscape in the Great Lakes area? 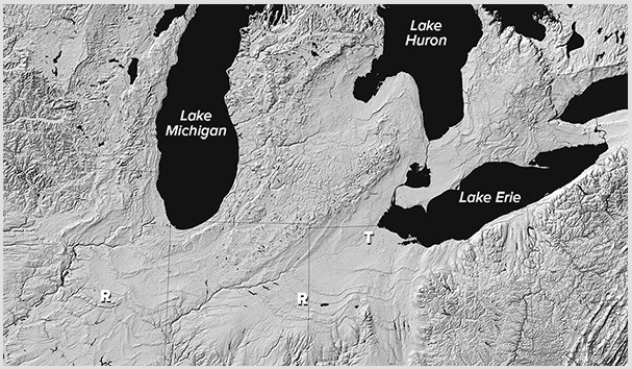
A) The areas were covered by soft marine sediments.
B) A huge flood coming from Iowa flowed toward the Great Lakes.
C) Glaciers carved out the smooth troughs.
D) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the upper surface of the open ocean freezes,the feature produced is called
A) sea ice,composed mostly of fresh water.
B) sea ice,composed mostly of salty water.
C) ice calving,composed mostly of fresh water.
D) ice calving,composed mostly of salty water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features labeled on this figure is an esker? 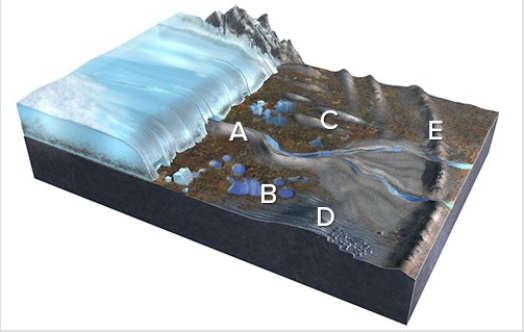
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the feature numbered 2 in the upper left part of this figure?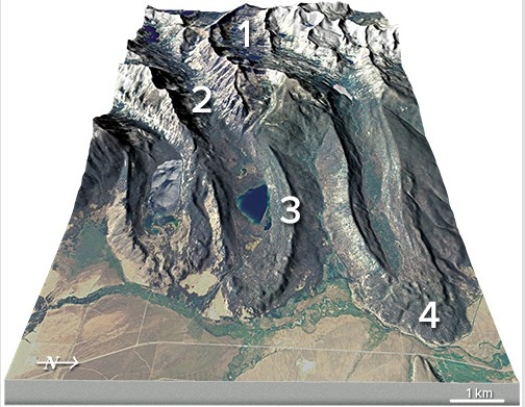 
A) Cirque
B) U-shaped valley
C) Lateral moraine
D) Terminal moraine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of glacier is shown below on the gently sloping land near the coastline? 
A) Tropical coast glacier
B) Shoreline glacier
C) Piedmont glacier
D) Continental ice sheet
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The present-day tilt of Earth's axis of rotation is 23.5°.What would be a result of more tilt,as shown here? 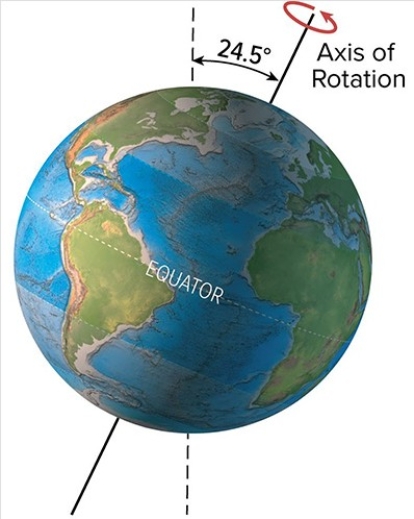
A) High latitudes would receive less direct sunlight during the summer,causing cooler temperatures
B) A decrease in glaciers
C) A decrease in the effects of the seasons
D) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features labeled on this figure is a kettle? 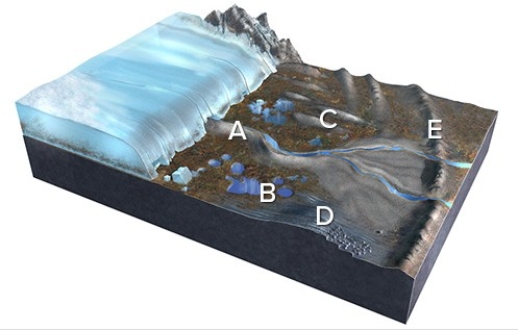
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are these sharp,glacially carved ridges? 
A) Cirque
B) Arête
C) Hogback
D) Razorback
E) Flatiron
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Abrasion is distinguished from plucking in that
A) abrasion is a smooth scraping,while plucking is a more jagged gouging of the bedrock.
B) abrasion is a jagged gouging,while plucking is a smooth scraping of the bedrock.
C) abrasion is an erosional feature,while plucking is a depositional feature.
D) abrasion is a depositional feature,while plucking is an erosional feature.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The exposed bedrock in the background of the figure below,to the right,formed as 
A) isostatic rebound caused the land to extend upward.
B) particularly resistant rock and/or thin ice left the rock above the ice surface.
C) a mantle hot spot melted the glacier in this localized area.
D) local wind-blown deposition concentrated in this area of the glacier.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do these teardrop-shaped hills (drumlins) record? 
A) Ancient lake levels
B) Piles of sediment recording past positions of the end of the glacier
C) Erosion and sculpting of soft materials by a moving glacier
D) Melting of large blocks of rock in the ice
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the feature numbered 3 in the center of this figure?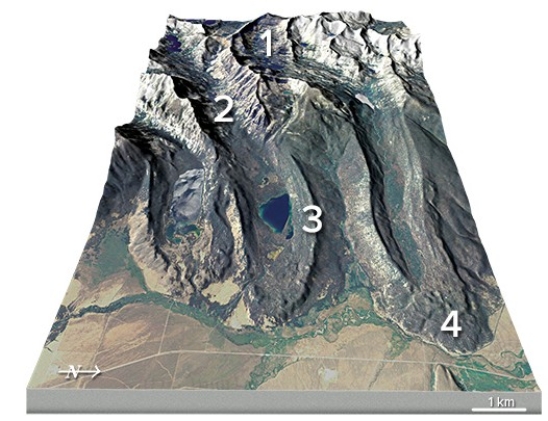 
A) Cirque
B) U-shaped valley
C) Lateral moraine
D) Terminal moraine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 75
Related Exams