A) In calculating the project's operating cash flows,the firm should not deduct financing costs such as interest expense,because financing costs are accounted for by discounting at the WACC.If interest were deducted when estimating cash flows,this would,in effect,"double count" it.
B) Since depreciation is a non-cash expense,the firm does not need to deal with depreciation when calculating the operating cash flows.
C) When estimating the project's operating cash flows,it is important to include both opportunity costs and sunk costs,but the firm should ignore the cash flow effects of externalities since they are accounted for in the discounting process.
D) Capital budgeting decisions should be based on before-tax cash flows because WACC is calculated on a before-tax basis.
E) The WACC used to discount cash flows in a capital budgeting analysis should be calculated on a before-tax basis.To do otherwise would bias the NPV upward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An example of a sunk cost is the cost associated with restoring the site of a strip mine once the ore has been depleted.
B) Sunk costs must be considered if the IRR method is used but not if the firm relies on the NPV method.
C) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where a bank opens a new office,and that new office leads to a decline in deposits of the bank's other offices.
D) A good example of a sunk cost is money that a banking corporation spent last year to investigate the site for a new office,then expensed that cost for tax purposes,and now is deciding whether to go forward with the project.
E) If sunk costs are considered and reflected in a project's cash flows,then the project's calculated NPV will be higher than it otherwise would have been had the sunk costs been ignored.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sensitivity analysis measures a project's stand-alone risk by showing how much the project's NPV (or IRR)is affected by a small change in one of the input variables,say sales.Other things held constant,with the size of the independent variable graphed on the horizontal axis and the NPV on the vertical axis,the steeper the graph of the relationship line,the more risky the project,other things held constant.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The primary advantage to using accelerated rather than straight-line depreciation is that with accelerated depreciation the total amount of depreciation that can be taken,assuming the asset is used for its full tax life,is greater.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Accelerated depreciation has an advantage for profitable firms in that it moves some cash flows forward,thus increasing their present value.On the other hand,using accelerated depreciation generally lowers the reported current year's profits because of the higher depreciation expenses.However,the reported profits problem can be solved by using different depreciation methods for tax and stockholder reporting purposes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors should be included in the cash flows used to estimate a project's NPV?
A) All costs associated with the project that have been incurred prior to the time the analysis is being conducted.
B) Interest on funds borrowed to help finance the project.
C) The end-of-project recovery of any additional net operating working capital required to operate the project.
D) Cannibalization effects,but only if those effects increase the project's projected cash flows.
E) Expenditures to date on research and development related to the project,provided those costs have already been expensed for tax purposes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two cardinal rules that financial analysts should follow to avoid errors are: (1)in the NPV equation,the numerator should use income calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,and (2)all incremental cash flows should be considered when making accept/reject decisions for capital budgeting projects.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rowell Company spent $3 million two years ago to build a plant for a new product.It then decided not to go forward with the project,so the building is available for sale or for a new product.Rowell owns the building free and clear--there is no mortgage on it.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since the building has been paid for,it can be used by another project with no additional cost.Therefore,it should not be reflected in the cash flows of the capital budgeting analysis for any new project.
B) If the building could be sold,then the after-tax proceeds that would be generated by any such sale should be charged as a cost to any new project that would use it.
C) This is an example of an externality,because the very existence of the building affects the cash flows for any new project that Rowell might consider.
D) Since the building was built in the past,its cost is a sunk cost and thus need not be considered when new projects are being evaluated,even if it would be used by those new projects.
E) If there is a mortgage loan on the building,then the interest on that loan would have to be charged to any new project that used the building.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relative risk of a proposed project is best accounted for by which of the following procedures?
A) Adjusting the discount rate upward if the project is judged to have above-average risk.
B) Adjusting the discount rate upward if the project is judged to have below-average risk.
C) Reducing the NPV by 10% for risky projects.
D) Picking a risk factor equal to the average discount rate.
E) Ignoring risk because project risk cannot be measured accurately.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statement completions is NOT CORRECT? For a profitable firm,when MACRS accelerated depreciation is compared to straight-line depreciation,MACRS accelerated allowances produce
A) Higher depreciation charges in the early years of an asset's life.
B) Larger cash flows in the earlier years of an asset's life.
C) Larger total undiscounted profits from the project over the project's life.
D) Smaller accounting profits in the early years,assuming the company uses the same depreciation method for tax and book purposes.
E) Lower tax payments in the earlier years of an asset's life.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Langston Labs has an overall (composite) WACC of 10%,which reflects the cost of capital for its average asset.Its assets vary widely in risk,and Langston evaluates low-risk projects with a WACC of 8%,average-risk projects at 10%,and high-risk projects at 12%.The company is considering the following projects: 
Which set of projects would maximize shareholder wealth?
Which set of projects would maximize shareholder wealth?
A) A and B
B) A,B,and C
C) A,B,and D
D) A,B,C,and D
E) A,B,C,D,and E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Temple Corp.is considering a new project whose data are shown below.The equipment that would be used has a 3-year tax life,would be depreciated by the straight-line method over its 3-year life,and would have a zero salvage value.No change in net operating working capital would be required.Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life.What is the project's NPV? Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number. 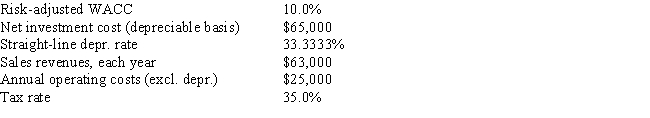
A) $14,825
B) $12,838
C) $18,340
D) $15,283
E) $17,729
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thomson Media is considering some new equipment whose data are shown below.The equipment has a 3-year tax life and would be fully depreciated by the straight-line method over 3 years,but it would have a positive pre-tax salvage value at the end of Year 3,when the project would be closed down.Also,additional net operating working capital would be required,but it would be recovered at the end of the project's life.Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life.What is the project's NPV? Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number. 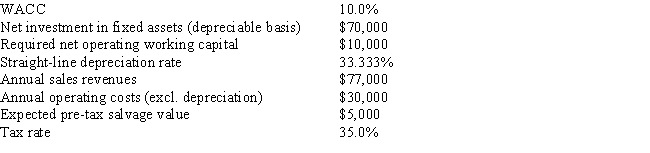
A) $26,238
B) $026,500
C) $020,728
D) $021,777
E) $028,861
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) A sunk cost is any cost that must be expended in order to complete a project and bring it into operation.
B) A sunk cost is any cost that was expended in the past but can be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
C) A sunk cost is a cost that was incurred and expensed in the past and cannot be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
D) Sunk costs were formerly hard to deal with,but once the NPV method came into wide use,it became possible to simply include sunk costs in the cash flows and then calculate the project's NPV.
E) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where Home Depot opens a new store,and that leads to a decline in sales of one of the firm's existing stores.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggarwal Enterprises is considering a new project that has a cost of $1,000,000,and the CFO set up the following simple decision tree to show its three most-likely scenarios.The firm could arrange with its work force and suppliers to cease operations at the end of Year 1 should it choose to do so,but to obtain this abandonment option,it would have to make a payment to those parties.How much is the option to abandon worth to the firm? 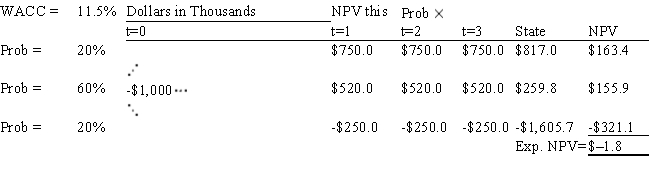
A) $77.8
B) $90.0
C) $64.8
D) $63.3
E) $76.3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Although it is extremely difficult to make accurate forecasts of the revenues that a project will generate,projects' initial outlays and subsequent costs can be forecasted with great accuracy.This is especially true for large product development projects.
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because of improvements in forecasting techniques,estimating the cash flows associated with a project has become the easiest step in the capital budgeting process.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The use of accelerated versus straight-line depreciation causes net income reported to stockholders to be lower,and cash flows higher,during every year of a project's life,other things held constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An externality is a situation where a project would have an adverse effect on some other part of the firm's overall operations.If the project would have a favorable effect on other operations,then this is not an externality.
B) An example of an externality is a situation where a bank opens a new office,and that new office causes deposits in the bank's other offices to decline.
C) The NPV method automatically deals correctly with externalities,even if the externalities are not specifically identified,but the IRR method does not.This is another reason to favor the NPV.
D) Both the NPV and IRR methods deal correctly with externalities,even if the externalities are not specifically identified.However,the payback method does not.
E) Identifying an externality can never lead to an increase in the calculated NPV.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The primary advantage to using accelerated rather than straight-line depreciation is that with accelerated depreciation the present value of the tax savings provided by depreciation will be higher,other things held constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 75
Related Exams