A) serine
B) glutamine
C) cysteine
D) glycine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The "cartoon" shown is an example of noncompetitive inhibition. 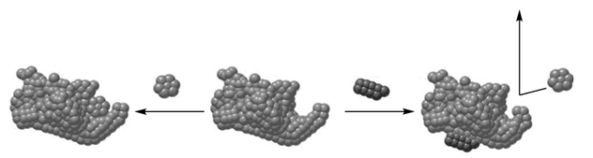
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tuftsin is a peptide that stimulate and promotes the destruction of tumor cells. Its primary structure is Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Which statement is NOT a valid interpretation of its primary structure?
A) It is a tetrapeptide.
B) Threonine is the N-terminal amino acid and arginine is the C-terminal amino acid.
C) The amino group of arginine is not joined to any other amino acid.
D) The carboxyl group of lysine is joined to the amino group of proline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many different dipeptides can be formed when one valine reacts with one glycine?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called a cofactor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The -helix and the -pleated sheet are examples of the tertiary structure of a protein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following forms of the amino acid valine (Val) . Which statement concerning these structures is false? 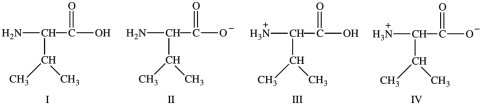
A) Structure I represents the form of Val present in blood at physiological pH.
B) Structure II represents the form of Val present in the basic environment of the intestines.
C) Structure III represents the form of Val present in the acidic environment of the stomach.
D) Structure IV represents the zwitterions of Val.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an example of a globular protein?
A) collagen
B) -keratin
C) hemoglobin
D) amylopectin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
-Keratin in hair is a fibrous protein composed almost exclusively of -helix units that wind together to form a superhelix.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a zymogen?
A) an amino acid with a neutral charge
B) inactive precursor of an enzyme
C) a molecule that causes an enzyme to lose activity
D) a nonprotein organic molecule needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The amide bonds in peptides and proteins are called peptide bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is not true?
A) A cofactor is always a metal ion needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur.
B) The names of most enzymes end in the suffix -ase.
C) An enzyme-catalyzed reaction can be 106 to 1012 times faster than a similar uncatalyzed reaction.
D) Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts for reactions in all living organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Serine exists primarily in its neutral form at a pH ~ 6.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The peptide leucylphenylalanylvalylvaline is abbreviated as Leu-Phen-Ala-Val-Val.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The -pleated sheet arrangement of a protein is favored by amino acids with small side chains.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The antibiotics penicillin and sulfanilamide, and drugs used to treat high blood pressure and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)are classified as coenzymes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Hydrogen bonding is possible between the side chains of the amino acids tyrosine and threonine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A dipeptide contains two amino acids joined together by two amide bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Zwitterions have low melting points and are water soluble.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the charge on an amino acid at a pH below its pI?
A) positive
B) neutral
C) negative
D) The charge or lack of charge varies depending on the amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 88
Related Exams