A) C.m/s
B) C.s/m
C) C/kg
D) kg/C.s
E) N/C.m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At any point the magnetic field lines are in the direction of:
A) the magnetic force on a moving positive charge
B) the magnetic force on a moving negative charge
C) the velocity of a moving positive charge
D) the velocity of a moving negative charge
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
J. J. Thomson's experiment, involving the motion of an electron beam in mutually perpendicular 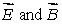 fields, gave the value of:
fields, gave the value of:
A) mass of electron
B) charge of electron
C) Earth's magnetic field
D) charge/mass ratio for electron
E) Avogadro's number
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron travels due north through a vacuum in a region of uniform magnetic field 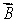 that is also directed due north. It will:
that is also directed due north. It will:
A) be unaffected by the field
B) speed up
C) slow down
D) follow a right-handed corkscrew path
E) follow a left-handed corkscrew path
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The magnetic force on a charged particle is in the direction of its velocity if:
A) it is moving in the direction of the field
B) it is moving opposite to the direction of the field
C) it is moving perpendicular to the field
D) it is moving in some other direction
E) never
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron is launched with velocity 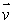 in a uniform magnetic field
in a uniform magnetic field 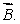 The angle between
The angle between  is between 0 and 90o. As a result, the electron follows a helix, its velocity vector
is between 0 and 90o. As a result, the electron follows a helix, its velocity vector 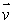 returning to its initial value in a time interval of:
returning to its initial value in a time interval of:
A) 2πm/eB
B) 2πmv/eB
C) 2πmv sin /eB
D) 2πmv cos /eB
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A proton (charge e) , traveling perpendicular to a magnetic field, experiences the same force as an alpha particle (charge 2e) which is also traveling perpendicular to the same field. The ratio of their speeds, vproton/valpha is:
A) 0.5
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A loop of current-carrying wire has a magnetic dipole moment of 5 *10-4 A .m2. The moment initially is aligned with a 0.5-T magnetic filed.To rotate the loop so its dipole momentt is perpendicular to the field and hold it in that orentation, you must do work of:
A) 0
B) 2.5 * 10-4 J
C) -2.5 * 10-4 J
D) 1.0 * 10-3 J
E) -1.0 * 10-3 J
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron enters a region of uniform perpendicular 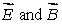 fields. It is observed that the velocity
fields. It is observed that the velocity 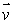 of the electron is unaffected. A possible explanation is:
of the electron is unaffected. A possible explanation is:
A) ![]() is parallel to
is parallel to ![]() and has magnitude E/B
and has magnitude E/B
B) ![]() is parallel to
is parallel to ![]()
C) ![]() is perpendicular to both
is perpendicular to both ![]() and has magnitude B/E
and has magnitude B/E
D) ![]() is perpendicular to both
is perpendicular to both ![]() and has magnitude E/B
and has magnitude E/B
E) the given situation is impossible
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron and a proton are both initially moving with the same speed and in the same direction at 90˚ to the same uniform magnetic field. They experience magnetic forces, which are initially:
A) identical
B) equal in magnitude but opposite in direction
C) in the same direction and differing in magnitude by a factor of 1840
D) in opposite directions and differing in magnitude by a factor of 1840
E) equal in magnitude but perpendicular to each other
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ion with a charge of +3.25*10−19 C is in region where a uniform electric field of 5 * 104. V/m is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.8 T. If its acceleration is zero then its speed must be:
A) 0
B) 1.6 * 104 m/s
C) 4.0 * 105 m/s
D) 6.3 * 105 m/s
E) any value but 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron (charge = -1.6 *10-19C) is moving at 3 *105 m/s in the positive x direction. A magnetic field of 0.8 T is in the positive z direction. The magnetic force on the electron is:
A) 0
B) 4 * 10-14 N in the positive z direction
C) 4 *10-14 N in the negative z direction
D) 4 * 10-14 N in the positive y direction
E) 4 * 10-14 N in the negative y direction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The direction of the magnetic field in a certain region of space is determined by firing a test charge into the region with its velocity in various directions in different trials. The field direction is:
A) one of the directions of the velocity when the magnetic force is zero
B) the direction of the velocity when the magnetic force is a maximum
C) the direction of the magnetic force
D) perpendicular to the velocity when the magnetic force is zero
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the formula 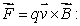
A) ![]() must be perpendicular to
must be perpendicular to ![]() but not necessarily to
but not necessarily to ![]()
B) ![]() must be perpendicular to
must be perpendicular to ![]() but not necessarily to
but not necessarily to ![]()
C) ![]() must be perpendicular to
must be perpendicular to ![]() but not necessarily to
but not necessarily to ![]()
D) all three vectors must be mutually perpendicular
E) ![]() must be perpendicular to both
must be perpendicular to both ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagrams show five possible orientations of a magnetic dipole 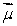 in a uniform magnetic field
in a uniform magnetic field  For which of these does the magnetic torque on the dipole have the greatest magnitude?
For which of these does the magnetic torque on the dipole have the greatest magnitude? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron is travelling in the positive x direction. A uniform electric field 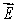 is in the negative y direction. If a uniform magnetic field with the appropriate magnitude and direction also exists in the region, the total force on the electron will be zero. The appropriate direction for the magetic field is:
is in the negative y direction. If a uniform magnetic field with the appropriate magnitude and direction also exists in the region, the total force on the electron will be zero. The appropriate direction for the magetic field is: 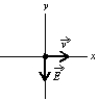
A) the positive y direction
B) the negative y direction
C) into the page
D) out of the page
E) the negative x direction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform magnetic field is in the positive z direction. A positively charged particle is moving in the positive x direction through the field. The net force on the particle can be made zero by applying an electric field in what direction?
A) Positive y
B) Negative y
C) Positive x
D) Negative x
E) Positive z
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A current is clockwise around the outside edge of this page and a uniform magnetic field is directed parallel to the page, from left to right. If the magnetic force is the only force acting on the page, the page will turn so the right edge:
A) moves toward you
B) moves away from you
C) moves to your right
D) moves to your left
E) does not move
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The units of magnetic dipole moment are:
A) ampere
B) ampere .meter
C) ampere .meter2
D) ampere/meter
E) ampere/meter2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform magnetic field is directed into the page. A charged particle, moving in the plane of the page, follows a clockwise spiral of decreasing radius as shown. A reasonable explanation is: 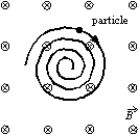
A) the charge is positive and slowing down
B) the charge is negative and slowing down
C) the charge is positive and speeding up
D) the charge is negative and speeding up
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 48
Related Exams