A) memory storage.
B) emotions.
C) balance and motor skills.
D) basal body functions such as heart function and respiratory rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a sensory receptor?
A) a nerve cell specialized to detect particular stimuli
B) a membrane protein that binds to a sensory ligand
C) the dendritic field of a sensory neuron
D) a specialized tissue like the eye
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemoreceptor is to taste as mechanoreceptor is to:
A) smell.
B) pain.
C) temperature.
D) sound.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding rhodopsin?
A) It is present in the photoreceptors of invertebrates and vertebrates.
B) It can be found in a cylindrical arrangement in the opsin transmembrane protein.
C) It contains retinal.
D) It can mediate the opening and closing of sodium channels.
E) It is both present in the photoreceptors of invertebrates and vertebrates AND can be found in a cylindrical arrangement in the opsin transmembrane protein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures would NOT contain sensory receptors?
A) the feet of a fruit fly
B) the bill of a platypus
C) the tongue of a dog
D) the skin of a human
E) None of the answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
White matter of the cerebrum contains:
A) neuronal cell bodies.
B) myelinated axons.
C) the respiratory centers.
D) midbrain structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which area of the brain are sound waves processed?
A) visual cortex
B) auditory cortex
C) cerebellum
D) somatosensory cortex
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diagram A below shows a stimulus applied to a sensory cell, and diagram B is the pattern of action potentials generated in response. 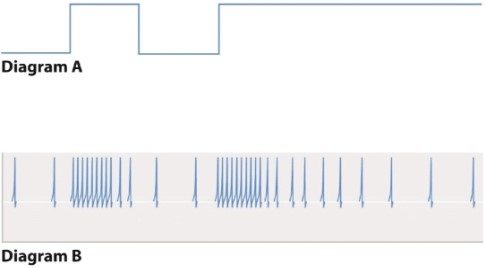 This pattern of action potentials:
This pattern of action potentials:
A) permits discrimination between different kinds of stimuli.
B) improves the simultaneous detection of two kinds of stimuli-for example, smell and taste.
C) allows an animal to constantly measure the strength of a continuing input.
D) allows an animal to detect the onset of a new stimulus. /12
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An interneuron may receive multiple stimuli from the same sensory neuron over a very short period of time. The firing rate of the receiving neuron is proportional to the number of signals received from the sensory neuron over time. Of which of the following is this an example?
A) temporal summation
B) spatial summation
C) action potential
D) hyperpolarization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Research suggests that learning may involve:
A) Ca2+ influx into a postsynaptic cell, causing biochemical changes and enhanced response to stimulation.
B) changes in action potential duration caused by blocking voltage-gated K+ channels.
C) strengthening the sodium-potassium pump.
D) synaptic changes caused by decreasing the size of the synaptic cleft and increasing the effectiveness of neurotransmitter diffusion.
E) synaptic changes causing slower reuptake of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of a tympanic membrane in insects and vertebrates is an example of:
A) divergent evolution.
B) coevolution.
C) convergent evolution.
D) adaptive radiation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Light entering a human eye travels through structures in this order:
A) cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina.
B) sclera, cornea, lens, aqueous humor, iris, vitreous humor, retina.
C) aqueous humor, iris, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina.
D) lens, cornea, vitreous humor, pupil, iris, aqueous humor, retina.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many insects can sense ultraviolet light. What is the evolutionary advantage of this ability?
A) the ability to detect predators and avoid predation
B) the ability to locate certain flowers for nectar, the insects' food source
C) the ability to avoid other flying insects that compete for food
D) the ability to sense balance and position during flight
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Another term that could be used to describe the chemosensitive hairs of an olfactory sensory neuron would be:
A) dendrites.
B) axons.
C) axon collaterals.
D) the cell body.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of olfaction and gustation?
A) Gustation is chemosensory, whereas olfaction is not.
B) Humans have more olfactory receptor proteins than gustation receptor proteins.
C) Gustation and olfaction signals are processed by the same cranial nerves supplying the brain.
D) Gustation is more sensitive to stimuli than olfaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of physical or chemical stimuli into nerve impulses is known as:
A) sensory transduction.
B) sensory reception.
C) motor response.
D) cellular response.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tympanic membrane of mammals is also known as the:
A) oval window.
B) cochlea.
C) vestibular system.
D) eardrum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man complains to his doctor that he has a very hard time smelling things. What could be the cause of this patient's poor sense of smell?
A) His olfactory sensory neurons lack chemosensitive hairs.
B) He has insufficient mucus production in his nasal cavity.
C) His olfactory-associated interneurons cannot fire action potentials.
D) Connections may not have developed between his olfactory-associated interneurons and sensory neurons.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is evidence that all animal vision has evolved from a common origin?
A) All animals use the same light-sensitive organs.
B) All animals use the photopigment opsin to sense light.
C) All animals have eyecups.
D) All animals have ommatidia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cone cells most likely evolved from:
A) rhodopsin.
B) retinal.
C) rod cells.
D) ommatidia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 205
Related Exams