A) 4
B) 8
C) 12
D) 16
E) 20
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following point mutations is unlikely to change a protein's ability to function?
A) one that occurs in a noncoding region of DNA
B) one that creates a new codon code for the same amino acid as the original codon
C) one that occurs in somatic cells
D) one that creates a new codon that codes for an amino acid of the same size as that coded for by the original codon
E) one that occurs in germ cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Any mutation that increases the risk of disease in an individual is known as a:
A) transmission mutation.
B) somatic mutation.
C) genetic load.
D) genetic risk factor.
E) predisposition factor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what situation can a harmful deletion in a chromosome persist in a population?
A) if it is homozygous
B) if the homologous chromosome lacks the deletion
C) if the deletion is not in the centromere, so it is not fatal.
D) if a transposon replaces the deleted region
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, which is less harmful, a duplication or deletion?
A) duplication
B) deletion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A family can share a genetic risk of developing cancer if:
A) the cancer is caused by somatic cell mutations.
B) the cancer is caused by germ-line mutations.
C) a germ-line mutation in one of the genes implicated in the cancer occurred in an ancestor.
D) a somatic cell mutation in one of the genes implicated in the cancer occurred in an ancestor.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Large chromosomal inversions can cause problems in which of the following processes?
A) meiosis
B) mismatch repair
C) reciprocal translocation
D) mitosis
E) None of the answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bacterial species that live entirely inside eukaryotic cells have deletions of genes for the synthesis of molecules that can be taken in from the host cell. This finding implies that the deletions are:
A) based on the needs of the organism, and these genes are not needed.
B) random, but that those that delete unneeded genes are not deleterious.
C) unlikely to have happened by chance.
D) induced by mutagens present inside the host cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ mutations affect only the individual in which they occur; _____ mutations are passed from parent to offspring.
A) Somatic; germ-line
B) Germ-line; somatic
C) Germ-line; heritable
D) Somatic; point
E) Point; germ-line
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about mutations is TRUE? A mutation:
A) may leave the amino acid sequence of a protein unchanged.
B) will result in a different phenotype.
C) will be corrected.
D) will be passed onto offspring.
E) None of the other answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
DNA ligase is responsible for repairing thymine dimers caused by UV light.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some people with blue eyes have a small sector of one eye that is brown. What kind of mutation could cause this color difference?
A) a somatic mutation in germ-line cells
B) a somatic mutation very early in development
C) a somatic mutation late in development
D) a germ-line mutation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A chemical agent that interferes with DNA repair may be considered a mutagen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic organisms with large genomes, the usual reason that many inversion breakpoints do not disrupt genes is because the breaks occur in:
A) the telomeres.
B) the centromere.
C) the nucleolus.
D) noncoding DNA.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transposable element can insert into any position in the genome EXCEPT:
A) regions near the telomere.
B) regions near the centromere.
C) regions near sequences that code for ribosomal RNA.
D) inside another transposon.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations would MOST likely have the most severe consequence?
A) silent
B) missense
C) frameshift
D) addition of a codon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In bacteria, many transposable elements are able to regulate their own transposition in such a way that the probability of transposition decreases as the number of copies of the transposon in a cell increases. If a transposon invades a bacterial cell that does not currently have any transposons, and then increases in copy number as the cell divides, what curve below would BEST depict the increase in copy number of such a self-regulating transposon? 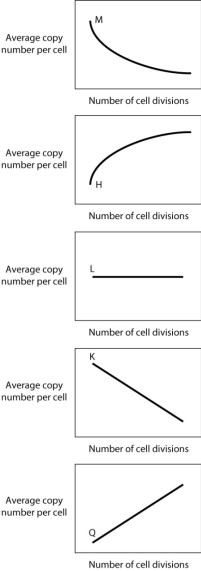
A) curve M
B) curve H
C) curve K
D) curve L
E) curve Q
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It has been estimated that the average human gamete contains about 30 new nucleotide-substitution mutations and approximately 3 new small insertions or deletions (indels) . Which of the following is/are TRUE?
A) The estimate must be wrong. Nobody could live with so many mutations.
B) Many of the mutations are likely to be in nonprotein coding DNA.
C) Most of the mutations have little or no effect on survival or health.
D) None of the other answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A point mutation that causes an amino acid replacement is called a:
A) synonymous (silent) mutation.
B) nonsynonymous (missense) mutation.
C) nonsense mutation.
D) stop mutation.
E) transition mutation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Spontaneous mutations that occur in somatic cells will be transmitted to offspring.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 165
Related Exams