A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The expected major product of the following reaction is: 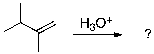
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Most bonds are quite susceptible to reaction with ____________________, also referred to as electron-seeking reagents.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following reaction sequence, identify the expected major organic products and provide their stereochemical relationship. 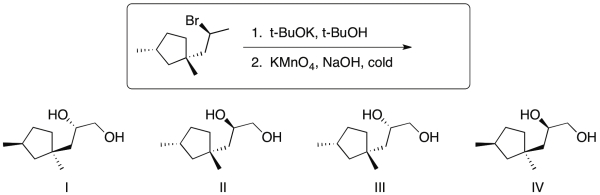
A) I and II; enantiomers
B) III and IV; enantiomers
C) I and II; diastereomers
D) II and III; diastereomers
E) III and IV; diastereomers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the alkenes shown, which would produce the product shown below, upon treatment with ozone, followed by zinc metal and water? 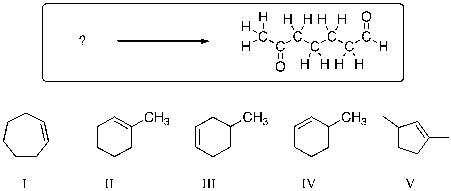
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the correct sequence of reaction steps necessary to complete the following transformation? 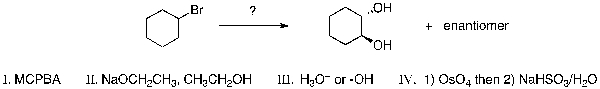
A) I then II then III
B) II then I then III
C) II then IV
D) III then I
E) I then IV then II then III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the expected major product for the following reaction sequence? 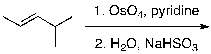
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
For the following transformation a) identify the starting material with correct stereochemistry and b) provide a complete reaction mechanism, including stereochemistry, to account for the product shown. 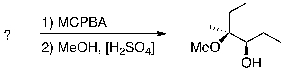
Correct Answer

verified
 Step 1 involves the epoxidation of the ...
Step 1 involves the epoxidation of the ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
For the following reaction sequence provide the expected major organic product(s). Include all stereoisomers showing relevant stereochemistry. 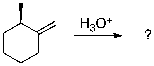
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The expected major product(s) of HCl addition to the alkene shown would be: 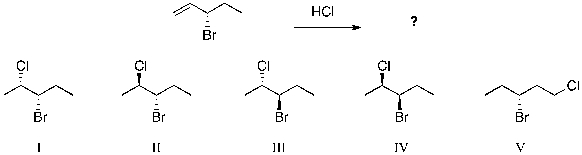
A) II
B) II and III
C) I and IV
D) V
E) All of the above are equally likely to form
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the expected major product of the following reaction sequence? 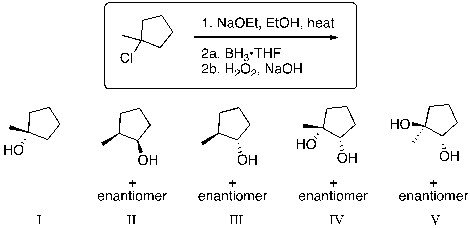
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Provide the organic product(s) for the reaction shown below. 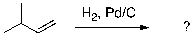
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
A common problem in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes is the formation of an ether byproduct. Explain the formation of the ether byproduct in relation to the reaction below: 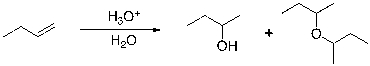
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction sequence shown, what is the expected major product? 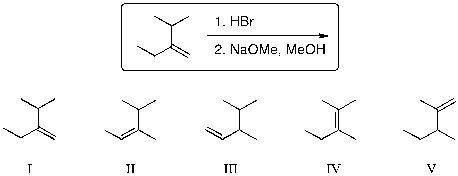
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of Br2 with 1-methylcyclohexene, in the presence of ethylamine (EtNH2) , is expected to produce which of the following as the major product? 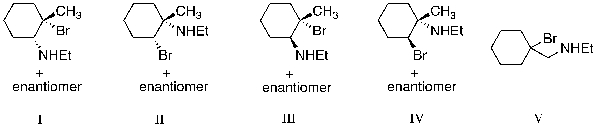
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw Fischer projections of the major product of the reaction between (Z)?2?methyl-3-hexene and aqueous Br2.
Correct Answer

verified
 The reaction takes place with anti ster...
The reaction takes place with anti ster...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the catalysts listed are used in the homogenous catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes? I) Ni II) Pt III) Wilkinson's catalyst
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and II
E) II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes the temperature dependence of an addition reaction?
A) Addition reactions are thermodynamically favored at all temperatures.
B) Addition reactions are thermodynamically disfavored at all temperatures.
C) Addition reactions are thermodynamically favored at low temperatures.
D) Addition reactions are thermodynamically favored at high temperatures.
E) Addition reactions are thermodynamically impossible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the expected major product(s) of the following reaction: 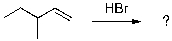
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) A and B
E) A and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw Fischer projection (s) of the major product(s) of the reaction between (Z)-3-methyl-3-hexene and MCPBA, followed by aqueous acid.
Correct Answer

verified
 The reaction takes place with...
The reaction takes place with...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Showing 81 - 100 of 148
Related Exams